Choosing the best way to heat your endless pool depends on your climate, budget, and energy goals. Heat pumps are energy-efficient and cost-effective for moderate climates, while gas heaters heat quickly and work well in colder areas. Solar systems are eco-friendly and save money long-term but require more upfront investment. Consider your usage and environment to find the best fit; more details can help you make a smart decision.
Key Takeaways
- Heat pumps are energy-efficient and ideal for moderate climates, reducing long-term costs with eco-friendly operation.
- Gas heaters provide quick, reliable warmth but have higher emissions and ongoing fuel costs.
- Solar heating offers the lowest operating costs and is environmentally friendly, best suited for sunny, warm areas.
- Consider climate, usage frequency, and budget when choosing to maximize efficiency and cost savings.
- Proper installation and maintenance are essential regardless of the heating method to ensure safety and performance.
How Heat Pumps Work and Their Benefits

Heat pumps work by transferring heat from one place to another, even in cold weather, making them an efficient heating and cooling option. They extract heat from the outside air and move it indoors to warm your space, or reverse the process to cool it down. This is achieved through a refrigeration cycle involving a compressor, evaporator, and condenser. Because they don’t generate heat but transfer it, heat pumps use less energy than traditional heating systems. This efficiency means lower energy bills and a smaller carbon footprint. Plus, they operate quietly and require minimal maintenance. Their versatility allows you to use them year-round, providing reliable comfort whether it’s hot or cold outside. Additionally, energy efficiency plays a crucial role in reducing environmental impact and operational costs. Overall, heat pumps offer an eco-friendly, cost-effective solution for climate control.
The Advantages and Disadvantages of Gas Heaters

Gas heaters provide a reliable and cost-effective way to warm your home, especially in areas where natural gas is readily available. They heat quickly and can maintain consistent water temperatures, making them ideal for frequent use. However, they come with disadvantages, such as higher emissions and the need for ventilation to prevent carbon monoxide buildup. Gas heaters also require regular maintenance to ensure safety and efficiency. Additionally, they are often favored for their seasonal versatility, allowing for effective heating year-round.
Exploring Solar Heating Systems for Endless Pools

If you’re looking for an energy-efficient way to keep your Endless Pool heated, solar heating systems offer a compelling option. They use sunlight to generate heat, making them environmentally friendly and cost-effective over time. Solar collectors, usually installed on your roof or nearby, capture sunlight and transfer heat to your pool water through a circulation system. These systems work best in sunny climates and during warmer months, but you can extend their usefulness with pool covers and auxiliary heating. Solar setups require an upfront investment for equipment and installation, but they can substantially reduce your energy bills. Maintenance is minimal, mainly involving system checks and ensuring collectors stay clean. Overall, solar heating provides a sustainable, eco-conscious way to enjoy your pool year-round. Additionally, selecting the right dog names can reflect your personality and style, just like choosing the best heating system for your pool.
Cost Comparison of Heat Pumps, Gas, and Solar Options

When comparing the costs of heating options for your Endless Pool, understanding the initial investment and ongoing expenses is key. Heat pumps usually have a higher upfront cost but lower operating expenses over time. Gas systems often require a moderate initial investment and have higher fuel costs, which can fluctuate. Solar systems typically involve a significant initial outlay, especially for installation and panels, but benefit from minimal ongoing costs. Additionally, some Hyundai Tuning modifications, like upgraded energy-efficient components, can influence overall energy consumption and savings.
Here’s a quick breakdown:
- Heat Pumps: Higher initial cost, lower monthly expenses.
- Gas: Moderate upfront, variable fuel costs.
- Solar: Highest initial investment, almost no fuel costs long-term.
Your choice depends on budget, local energy prices, and long-term savings.
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Impact of Each Method

You’ll want to contemplate how much energy each method uses and their overall impact on the environment. Comparing their carbon footprints reveals which options are greener choices. Additionally, integrating renewable energy sources can markedly improve their efficiency and reduce emissions. Considering advancements in heat pump technology, such as smart controls and variable speed compressors, can further enhance energy savings and sustainability.
Power Consumption Levels
Heat pumps generally consume less energy than traditional heating methods, making them a more efficient choice for many households. They transfer heat rather than generate it, notably reducing power use. When comparing power consumption levels, consider these key points:
- Efficiency Ratings: Heat pumps typically have higher COP (Coefficient of Performance) values, meaning they produce more heat per unit of electricity than gas or solar systems.
- Operational Costs: Due to lower energy needs, heat pumps usually cost less to operate over time compared to gas or solar setups.
- Environmental Impact: While solar systems can use minimal power, heat pumps still rely on electricity, which can be generated from renewable sources, further reducing environmental impact.
- Energy Efficiency and Environmental Impact: The overall sustainability of each method depends on your local energy sources and infrastructure, influencing their environmental benefits.
Choosing the right method depends on your energy needs, local costs, and available resources.
Carbon Footprint Comparison
Which heating method leaves the smallest carbon footprint? Generally, solar heating produces the least emissions because it relies on renewable energy, reducing greenhouse gases. Heat pumps are highly efficient, using less electricity than traditional electric heaters, so their carbon footprint depends on your grid’s energy sources. If your electricity comes from clean energy, heat pumps are environmentally friendly. Gas heating, on the other hand, releases more carbon dioxide directly into the atmosphere, making it less eco-friendly. While gas may be cost-effective, it has a higher environmental impact. Solar and heat pumps, especially when paired with renewable energy sources, substantially cut your home’s carbon emissions. Your choice depends on local energy infrastructure, but overall, solar and heat pumps tend to be greener options. Additionally, hydrogen energy can serve as a clean alternative in certain applications, further reducing overall environmental impact.
Renewable Energy Integration
How effectively each heating method integrates renewable energy markedly impacts its environmental footprint and efficiency. Solar heating directly harnesses sunlight, making it the most sustainable option if ample sunlight is available. Heat pumps can utilize renewable electricity, reducing reliance on fossil fuels when powered by clean energy sources. Gas heating, however, relies on non-renewable resources, limiting its sustainability. To evaluate these methods:
- Solar systems depend on geographic location and sunlight availability, offering high renewable integration where conditions are favorable.
- Heat pumps’ efficiency improves when paired with renewable electricity, minimizing emissions.
- Gas heating provides limited renewable integration, resulting in higher environmental impact and lower overall efficiency.
- Implementing systems that leverage renewable energy sources can significantly enhance the sustainability of your heating solution.
Your choice should consider local renewable energy infrastructure and the potential for integrating sustainable sources.
Climate Considerations for Heating Choices

The climate of your location plays a crucial role in determining the most efficient and sustainable heating solution. In colder regions, gas heaters or high-capacity heat pumps perform better because they can generate more heat efficiently despite low temperatures. If you live in a mild or warm climate, solar heating or simple heat pump systems might be sufficient, reducing energy costs. Extremely cold climates may require a backup system, like gas, to maintain consistent water temperatures. Conversely, in sunny areas, solar heating can be highly effective, especially if you have ample sunlight year-round. Understanding your area’s temperature ranges and seasonal variations helps you choose a system that maximizes efficiency and minimizes operational costs. Tailoring your selection to your climate ensures excellent performance and long-term savings. Additionally, considering renewable energy innovations can further enhance your pool heating options and sustainability.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
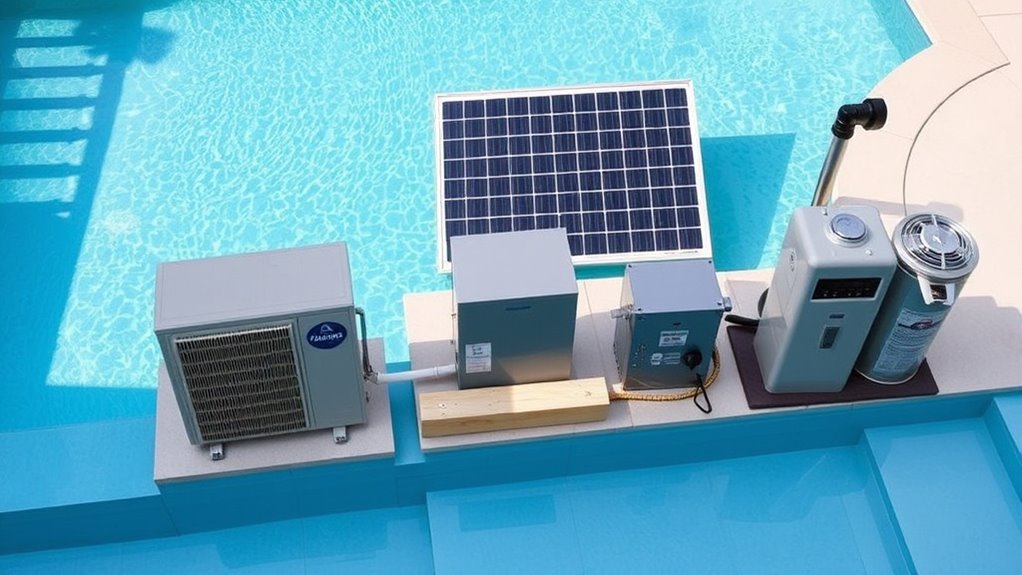
Choosing the right heating system also involves understanding the installation process and ongoing maintenance it requires. Each option has unique demands that can impact your pool’s operation and longevity. For instance, regular filter cleaning and system checks are necessary for heat pumps to maintain efficiency. Exfoliation benefits can also influence how often components like filters need replacement or servicing, especially if algae or debris buildup occurs. 1. Heat Pumps: Installing a heat pump involves proper electrical wiring and ensuring adequate ventilation. Regular filter cleaning and system checks are necessary for efficiency. 2. Gas Heaters: Gas units require professional installation for safe connection to your gas supply and proper venting. Maintenance includes inspecting for leaks and cleaning burners periodically. 3. Solar Heaters: Solar systems need roof or ground mounting, along with professional setup to optimize sunlight exposure. Maintenance mainly involves cleaning panels and checking for debris or shading. Understanding these requirements helps you plan for a safe, efficient, and long-lasting installation.
Budget-Friendly Options and Long-Term Savings

Choosing the right heating option can save you money upfront and over the years. Affordable installation choices can reduce your initial costs, while energy-efficient systems lower your bills long-term. Let’s explore how to balance upfront expenses with ongoing savings to find the best fit for your budget.
Cost-Effective Installation Choices
When evaluating heating and cooling options, prioritizing cost-effective installation choices can save you money upfront and reduce expenses over time. To maximize savings, consider these options:
- Opt for DIY installation when feasible, lowering labor costs and providing quick setup.
- Choose modular or scalable systems, allowing you to expand or upgrade as needed without costly overhauls.
- Select energy-efficient equipment compatible with existing infrastructure to minimize installation complexity and long-term operating costs.
Energy Savings Over Time
While initial installation costs are important, focusing on energy savings over time can lead to substantial long-term financial benefits. Heat pumps, solar heaters, and gas options vary considerably in ongoing energy expenses. Heat pumps generally consume less electricity than traditional electric heaters, saving you money over years of use. Solar heating, though costly upfront, offers near-zero operating costs once installed, dramatically reducing your energy bills. Gas heaters may have moderate operating costs but can be more economical than electric options depending on local fuel prices. By choosing energy-efficient systems and optimizing usage, you can lower your bills and reduce environmental impact. Over time, these savings add up, making a more energy-conscious choice worthwhile for your budget and the longevity of your pool.
Making the Right Choice for Your Pool and Lifestyle

Selecting the best heating option for your pool depends on how you plan to use it and your lifestyle. Consider these factors to make the right choice:
- Frequency of use: If you swim frequently, investing in a reliable, cost-effective system like a heat pump or solar may save you money long-term.
- Climate: Colder climates benefit from gas heaters for quick, powerful heating, while warmer regions suit solar or heat pumps.
- Budget and sustainability goals: Gas offers quick heating but higher operational costs, while solar and heat pumps are eco-friendly and reduce energy bills over time.
Evaluate how often and how long you’ll use your pool, your local climate, and your financial priorities. This will guide you toward the most suitable, efficient heating solution for your lifestyle.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which Heating Method Is Most Effective in Extreme Weather Conditions?
In extreme weather, gas heaters are your best choice because they quickly and reliably heat your pool regardless of outside temperatures. They work efficiently in very cold conditions and can maintain consistent water warmth. Heat pumps and solar options struggle in extreme cold, making gas the most effective solution. You’ll enjoy warm water year-round with a gas heater, even during harsh winter weather.
How Do Seasonal Variations Affect Each Heating Option’s Performance?
You might think seasonal changes don’t impact pool heating, but they do. During colder months, heat pumps work harder and consume more energy, potentially lowering efficiency. Gas heaters provide consistent warmth regardless of season but at higher costs. Solar heating depends heavily on sunlight; its performance drops markedly in winter. So, your choice should consider seasonal variations, ensuring reliable heating year-round without surprises.
Can Multiple Heating Systems Be Combined for Efficiency?
Yes, you can combine multiple heating systems to boost efficiency and reliability. For example, use a heat pump as your primary source for most of the year, and switch to gas or solar backup during peak demand or colder months. This setup guarantees continuous, cost-effective heating, reduces energy waste, and maximizes overall system lifespan. Just make sure to coordinate the systems properly to avoid conflicts or inefficiencies.
What Safety Considerations Are Associated With Each Heating Method?
Think of each heating method as a different safety gear—like a helmet, gloves, or knee pads. Gas heaters pose fire and carbon monoxide risks, so make certain proper ventilation and regular inspections. Heat pumps and solar systems are safer but require electrical safety checks. I once saw a pool owner install a solar heater without grounding; it risked electrical shock. Always follow manufacturer guidelines and have professional inspections for safe operation.
How Do Maintenance Costs Compare Over the System’s Lifespan?
You’ll find that heat pumps generally have lower maintenance costs over their lifespan because they have fewer moving parts and require less frequent servicing. Gas systems might cost more to maintain due to regular inspections and part replacements. Solar heating systems tend to have minimal ongoing costs, mainly for occasional cleaning and inspection, but initial setup can be expensive. Overall, heat pumps are usually the most economical option for long-term maintenance.
Conclusion
Choosing the right heating method for your endless pool is like picking the perfect sailing route—you want smooth sailing and steady comfort. Whether you opt for a heat pump, gas, or solar, understanding each option’s benefits helps you steer wisely. I once watched a homeowner switch from gas to solar and save hundreds annually, proving that the right choice can turn your pool into a relaxing, eco-friendly oasis—making every swim a breeze.